- Born: February 7, 1812, Landport
- Died: June 9, 1870, Higham, United Kingdom
- Plays: A Tale of Two Cities, No Thoroughfare, The Frozen Deep, A Christmas Carol, The Goblins
- Influenced by: William Shakespeare, Victor Hugo
- Short stories: The Signalman, The Haunted House
Writing saved Dickens, both financially and emotionally. As an adult, he set his life’s work on exposing social ills, using his boundless talents and energies to spin engaging, poignant tales from the streets. In doing so, he also introduced new accessible forms of publishing that proved immensely popular and influential. Dickens’s keen observational style, precise description, and sharp social criticism have kept his large body of work profoundly enduring.
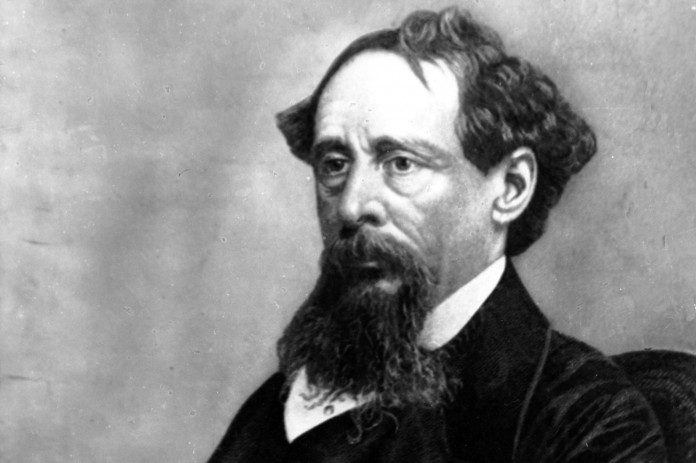
Charles Dickens (Charles John Huffam Dickens) was born in Landport, Portsmouth, on February 7, 1812. Charles was the second of eight children to John Dickens (1786–1851), a clerk in the Navy Pay Office, and his wife Elizabeth Dickens (1789–1863). The Dickens family moved to London in 1814 and two years later to Chatham, Kent, where Charles spent early years of his childhood. Due to the financial difficulties they moved back to London in 1822, where they settled in Camden Town, a poor neighborhood of London.
The defining moment of Dickens’s life occurred when he was 12 years old. His father, who had a difficult time managing money and was constantly in debt, was imprisoned in the Marshalsea debtor’s prison in 1824. Because of this, Charles was withdrawn from school and forced to work in a warehouse that handled ‘blacking’ or shoe polish to help support the family. This experience left profound psychological and sociological effects on Charles. It gave him a firsthand acquaintance with poverty and made him the most vigorous and influential voice of the working classes in his age.
After a few months Dickens’s father was released from prison and Charles was allowed to go back to school. At fifteen his formal education ended and he found employment as an office boy at an attorney’s, while he studied shorthand at night. From 1830 he worked as a shorthand reporter in the courts and afterwards as a parliamentary and newspaper reporter.
In 1833 Dickens began to contribute short stories and essays to periodicals. A Dinner at Popular Walk was Dickens’s first published story. It appeared in the Monthly Magazine in December 1833. In 1834, still a newspaper reporter, he adopted the soon to be famous pseudonym Boz. Dickens’s first book, a collection of stories titled Sketches by Boz, was published in 1836. In the same year he married Catherine Hogarth, daughter of the editor of the Evening Chronicle. Together they had 10 children before they separated in 1858.
Although Dickens’s main profession was as a novelist, he continued his journalistic work until the end of his life, editing The Daily News, Household Words, and All the Year Round. His connections to various magazines and newspapers gave him the opportunity to begin publishing his own fiction at the beginning of his career.
The Posthumous Papers of the Pickwick Club was published in monthly parts from April 1836 to November 1837. Pickwick became one of the most popular works of the time, continuing to be so after it was published in book form in 1837. After the success of Pickwick Dickens embarked on a full-time career as a novelist, producing work of increasing complexity at an incredible rate: Oliver Twist (1837-39), Nicholas Nickleby(1838-39), The Old Curiosity Shop and Barnaby Rudge as part of the Master Humphrey’s Clock series (1840-41), all being published in monthly instalments before being made into books.
In 1842 he travelled with his wife to the United States and Canada, which led to his controversial American Notes (1842) and is also the basis of some of the episodes in Martin Chuzzlewit. Dickens’s series of five Christmas Books were soon to follow; A Christmas Carol (1843), The Chimes(1844), The Cricket on the Hearth (1845), The Battle of Life(1846), and The Haunted Man (1848). After living briefly abroad in Italy (1844) and Switzerland (1846) Dickens continued his success with Dombey and Son (1848), the largely autobiographical David Copperfield (1849-50), Bleak House (1852-53), Hard Times (1854), Little Dorrit (1857), A Tale of Two Cities (1859), and Great Expectations (1861).
In 1856 his popularity had allowed him to buy Gad’s Hill Place, an estate he had admired since childhood. In 1858 Dickens began a series of paid readings, which became instantly popular. In all, Dickens performed more than 400 times. In that year, after a long period of difficulties, he separated from his wife. It was also around that time that Dickens became involved in an affair with a young actress named Ellen Ternan. The exact nature of their relationship is unclear, but it was clearly central to Dickens’s personal and professional life.
In the closing years of his life Dickens worsened his declining health by giving numerous readings. During his readings in 1869 he collapsed, showing symptoms of mild stroke. He retreated to Gad’s Hill and began to work on Edwin Drood, which was never completed.
Charles Dickens died at home on June 9, 1870 after suffering a stroke. Contrary to his wish to be buried in Rochester Cathedral, he was buried in the Poets’ Corner of Westminster Abbey. The inscription on his tomb reads:
“He was a sympathiser to the poor, the suffering, and the oppressed; and by his death, one of England’s greatest writers is lost to the world.”
Novels
1:The Pickwick Papers – 1836
2:Oliver Twist – 1837
3:Nicholas Nickleby – 1838
4:The Old Curiosity Shop – 1840
5:Barnaby Rudge – 1841
6:Martin Chuzzlewit – 1843
7:Dombey and Son – 1846
8:David Copperfield – 1849
9:Bleak House – 1852
10:Hard Times – 1854
11:Little Dorrit – 1855
12:A Tale of Two Cities – 1859
13:Great Expectations – 1860
14:Our Mutual Friend – 1864
15:The Mystery of Edwin Drood – 1870
Short stories and other works
1:American Notes
2:The Battle of Life
3:The Chimes: A Goblin Story
4:A Christmas Carol
5:A Christmas Tree
6:A Dinner at Poplar Walk
7:Doctor Marigold’s Prescriptions
8:A Flight
9:Frozen Deep
10:George Silverman’s Explanation
11:Going into Society
12:The Haunted Man
13:Holiday Romance
14:The Holly-Tree
15:Hunted Down
16:The Long Voyage
17:Master Humphrey’s Clock
18:A Message from the Sea
19:Mrs. Lirriper’s Legacy
20;Public Life of Mr. Trumble, Once Mayor of Mudfog
21:Sketches by Boz
22:The Story of the Goblins Who Stole a Sexton
23:Sunday under Three Heads
24:Tom Tiddler’s Ground
25:Travelling Abroad – City of London Churches
26:The Uncommercial Traveller
27:Wreck of the Golden Mary
References
N.A.(2013). Charles dickens biography. Charles dickens online. Retrieved on 04 July, 2014 from
http://www.dickens-online.info/charles-dickens-biography.htm
N.A (2012). Charles dickens: biography. WGBH Educational foundation. Retrieved on 04 July, 2014 from http://d43fweuh3sg51.cloudfront.net/media/assets/wgbh/gtexp12/gtexp12_doc_dickensbio/gtexp12_doc_dickensbio.pdf
N.A (2015) Charles dickens. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 04 July, 2015 from
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/charles- dickens















nice