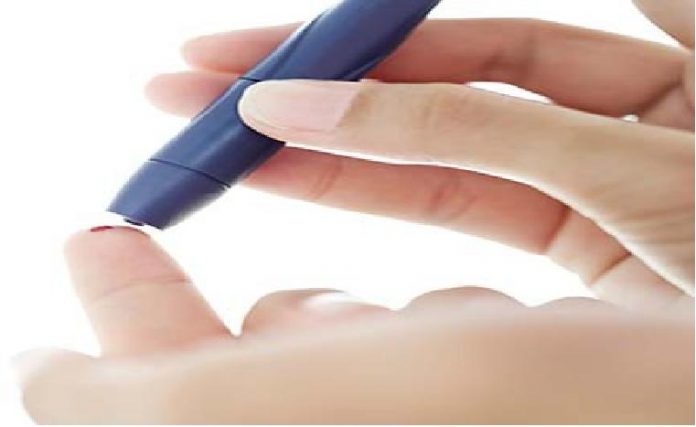
The other day I asked one of my accomplished friends, “Do you have diabetes?” “No,” he replied instantaneously. “Have you ever checked your blood glucose?” “No, but I am fine.” Well I continued, “How are you so confident that you don’t have diabetes?” (Grins!!!) “Have you any family member with diabetes?” “Yes, my mother.” “How was she diagnosed?” “She had to undergo a minor surgical procedure and before surgery doctor advised for blood glucose!!!” This is not a mere anecdote; this is a fact and an eye opener for all of us. Health consciousness is the need of the hour, lest it will be too late.
Everybody must have heard about diabetes, each of us may have a family member or a relative or a friend who has diabetes. But how many of us know some simple things about diabetes like what is diabetes? What do we need to do to control it? How can we prevent diabetes? Many highly qualified persons with long standing diabetes don’t even know the basics of their disease, though they have a smart phone with 4G network in their pockets! Please don’t tell me that it is the domain of doctor, in the present world of information technology we can’t afford to remain ignorant about diabetes. A person with diabetes must take proactive role in the management of his/her diabetes. He/she is the most important member of Diabetes Management Team and doctor is not the boss but the facilitator. This article is an attempt in this regard and I firmly believe that it will help many conscious minds.
What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by persistent elevation of glucose level in the blood. This elevated blood glucose level over a period of years causes damage to all organs of body especially eyes, kidneys, heart, nerves, blood vessels. Infact diabetes is the most common cause of blindness, renal failure, heart attacks, strokes and foot amputations.
How does diabetes occur?
Insulin is a hormone secreted by beta cells of pancreas. Insulin is needed for entry of glucose from blood into the cells. In patients with diabetes there is a defect in insulin production or insulin secretion or insulin action.
In patients with type 2 diabetes (T2DM), there is a defect in insulin secretion from beta cells of pancreas. This type of diabetes is usually seen in adults. Such individuals are treated with oral antidiabetic medication. These medicines don’t lower blood glucose by themselves (directly). Actually, these medicines act on beta cells of pancreas and cause release of insulin from them which then lowers blood glucose level.T2DM patients also have defect in insulin action (insulin resistance) and many oral anti diabetic medication improves insulin action as well.
However, in patients with type 1 diabetes (T1DM) beta cells of pancreas get destroyed and there is absolute deficiency of insulin in the body. This type of diabetes is usually seen in children. As there is no insulin present in their body, oral antidiabetic medication are not effective in them and hence they need insulin throughout their life.
What are the risk factors for diabetes?
Risk factors for diabetes are divided into two
Non modifiable risk factors for diabetes.
- Age: As age of a person increases, the risk of developing diabetes increases.
- Race/Ethinicity: Prevalence of diabetes is more in Asians and Africans than in Caucasians (Americans and Europeans)
- Family history of diabetes:
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (diabetes that develops during pregnancy)
- Modifiable risk factors for diabetes.
- Over weight/ obesity
- Lack of physical activity
- Lack of vegetables/fruits in diet
- Excessive use of soft drinks
How can we prevent developing diabetes?
Knowing modifiable risk factors for diabetes and trying to rectify them will help in decreasing the risk of developing diabetes.
Obesity being the most important modifiable risk factor for diabetes, one should toil (try) to achieve an ideal body weight. A simple formula to know ones ideal body weight is height (cms) – 100. For instance, if an individual’s height is 160cm, his weight should be 160-100 = 60 kg. Individuals who are overweight must decrease oil consumption, decrease size of their food servings and say no to soft drinks and junk food.
Lack of exercise is also important risk factor developing diabetes. Moderate intensity exercise for 150mins/week, in at least 5 sessions is necessary. Moderate intensity is defined as achieving 70% of maximal heart rate (Maximal heart rate = 220-Age). For instance for a 50 year individual, maximal heart rate will be 220-50 = 170 beats per minute and 70% of this will be 120 beats/min. In short one should do brisk walk for 20-30mins per day (one should feel his/her heart beating and sweat a bit).
Excessive use of soft drinks leads to obesity which inturn increases the risk of developing diabetes
Symptoms of diabetes
- Excessive thirst/ Dryness of mouth
- Frequent urination
- Excessive hunger
- Weightloss
- Frequent boils
- Burning of hands and feet
- Genital itching
Many individuals with diabetes do not have any of the above mentioned symptoms or they are mild and do not disturb their routine activities. Such individuals live with uncontrolled diabetes for years and may present first time with complications of diabetes like renal failure, heart attack, stroke, foot ulcer or diminution of vision. So all adults (>20 years of age) must get themselves screened for diabetes.
How is diabetes diagnosed?
Screening involves checking 2 blood samples one in fasting state (no food intake for at least 8 hours) and second blood sample 2 hours after ingesting 75g of glucose. This is called oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT).
Interpretation of OGTT
Fasting plasma glucose (mg/dL) Plasma glucose 2 hours after 75g glucose ingestion (mg/dL) Interpretation
< 100 <140 Normal (No diabetes)
100-125 140-199 Prediabetes
≥ 126 ≥ 200 Diabetes
Note
- Those having normal OGTT should repeat same after 3 years as chances of developing diabetes in next 3 years are minimal.
- Those having prediabetes should repeat test after 1 year. They should reduce weight if overweight and do exercise as discussed above to prevent or delay the development of frank diabetes.
- Those having diabetes on OGTT should repeat test once again to confirm same. If repeat testing confirms diabetes they should reduce weight if overweight and do exercise and consult doctor.
- If a person is having symptoms suggestive of diabetes, a single abnormal OGTT confirms the diagnosis of diabetes.
Treatment of T2DM
Treatment of T2DM involves life style modifications and medication. Lifestyle modifications are as important as medication. Life style measures revolve around achieving ideal body weight by dietary modifications and adopting a regular exercise protocol as already discussed above under prevention of diabetes. Those individuals who do not achieve targets with life style measures need medication as well. Initially they require one or 2 tablets however as the duration of diabetes increases they need more number of medications. This is because of the fact that diabetes is a progressive disease and over years beta cells become weaker and weaker and oral medication become less effective. After 10 to 15 years of duration of disease, they need insulin as well.
It is important to mention here that people should not delay initiation of insulin if targets are not achieved with maximal doses of oral medication. As for as damage to organs due to elevated blood glucose is concerned, each day counts and decision must be based on rationality and in light of evidence (world research in diabetes) and must not be delayed.
Treatment goals for adults with diabetes
- Sugar control
- Fasting/before meal sugar level 70 – 130 mg/dl
- Post prandial (2 Hours after food) sugar level < 180 mg/dl
- HbA1c Level < 7 %
- Blood Pressure < 130/80 mmHg
- Lipids Profile
- LDL (Bad Cholesterol) < 100 mg/dl
- HDL (Good Cholesterol) > 40 mg/dl (Men) & > 50mg/dl (Women)
- Triglycerides < 150mg/dl
What is HbA1c?
HbA1c indicates the average blood glucose levels over preceding 3 months. It is the most important target in diabetes. It is often neglected, which is unfortunate and definitely far from comprehensiveness. HbA1c should be measured at least twice a year for those who are meeting their treatment goals and have stable glycemic control.
What is the monitoring plan for a patient with diabetes?
The following is the simplest monitoring plan for a patient of T2DM who is on oral antidiabetic medication
- Daily: Self feet examination
- Monthly: Fasting blood glucose and post prandial glucose
- 4 monthly: Weight, Blood pressure measurement, HbA1c level
- Annually: Detailed foot examination by doctor; Eye checkup by ophthalmologist; KFT, Urine microalbumin; ECG, Lipid profile
(Note I have not detailed regarding type 1 diabetes seen in children or gestational diabetes during pregnancy, they are all together different topics and will be dealt in future.)
So what is the road ahead? We need to know diabetes to manage it in a better way and live a worry free life. There is no alternative to it. If ignored, diabetes is a silent killer. In fact, every 10 seconds one person dies of diabetes and every 10 seconds two persons develop diabetes. Therefore, I request every reader to get his /her blood glucose checked and interpret the report themselves and take necessary action. If needed he/she should consult a doctor at their local health facility. It is also my humble request to every reader to discuss about screening for diabetes in family, friend circle, offices and wherever we work so that more and more people become aware and get benefitted. Together we can overcome diabetes and make a healthier society. I end with the same question for the reader, “Do you have diabetes?”
REFERENCE:
Jan 3 2017.Get yourself checked.Greater Kashmir.retrieved from
http://www.greaterkashmir.com/news/opinion/story/237803.html